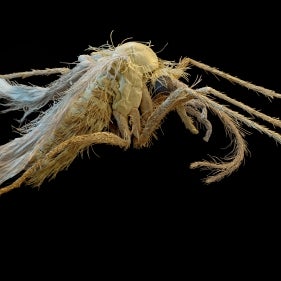
CVBD Companion Vector-Borne Diseases are a growing global threat
Transmitted by numerous so-called vectors, these diseases are known to veterinarians throughout the world and in some cases also have zoonotic consequences.
See diseasesSee vectorsCOMPANION VECTOR-BORNE DISEASES
EXPLORE OUR CONTENT
 CVBD MapsThe CVBD Occurence World Map presents country-specific situations based on current scientific knowledge and feed-back from experts around the world in an easy-to-grasped way. |
| Read more-> |
 ResourcesElanco Animal Health supports education in parasitology and especially in the field of vector-borne diseases. Access image collections, discover the World Forum calendar, interesting links and our glossary. |
| Read more-> |
 CVBD World ForumThe CVBD World Forum is a working group of leading international experts with the mission to enhance knowledge and communication on companion animal vector-borne diseases for the improvement of animal, human, and environmental health. |
| Read more-> |